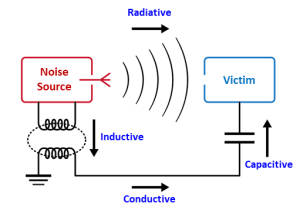
When two devices influence each other with electromagnetic waves, the one that affects the other is called a ‘noise source’, and the one that gets affected is called a ‘victim’. To obtain EMC certificates, the product should neither emit greater electromagnetic noise than the standard to become a noise source nor be prone to external interference to become a victim.
What is EMC?
EMC stands for ElectroMagnetic Compatibility, which is the ability of electrical equipment to function acceptably in their electromagnetic environment by limiting the unintentional generation, propagation, and reception of electromagnetic energy, which may cause unwanted effects like electromagnetic interference (EMI) in the equipment.
Quality assurance test for EMC is standardized and formulated by each country: for example, KC of Korea, FCC of the United States, and CE of EU. Electronic products must pass specific quality assurance tests to start merchandising in other countries. Therefore it is necessary to design and manufacture products carefully inside the standards.
| Country | Certification/Supervisory Authority | Certificate Logo |
|---|---|---|
| Korea | Ministry of Science and ICT National Radio Research Agency |
 |
| USA | Federal Communications Commission |  |
| EU | European Organization for Testing and Certification |  |
| Japan | Voluntary Control Council for Interference (VCCI) |  |
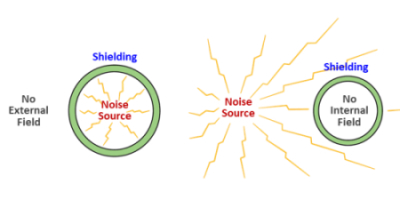
Significance of EMI Shielding
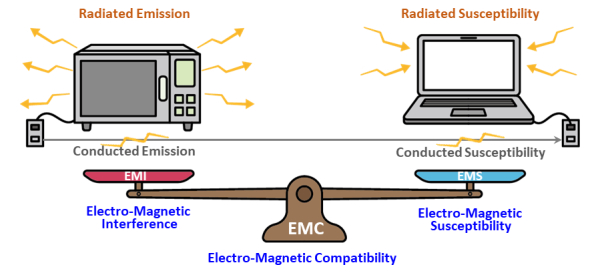
RE Test and RS Test
Not to be the noise source. RE Test, Radiated Emission Test, is a test to measure the intensity of electromagnetic signals the device emits in operation. Each country enforces different standards for RE Test for each frequency band, and it is necessary to apply a noise-reductive design when the noise emission is greater than the standard. This noise-reductive design is called ‘EMI solution’, including EMI shielding and EMI absorbing (EMI suppression).
Not to be the victim. RS Test, Radiated Susceptibility Test, is a test to measure the degree of malfunction resistance against incoming electromagnetic waves greater than the standards. This noise resistance design is called ‘EMS solution’.
The integrated term of EMI and EMS is called ‘EMC solution’. EMI and EMS controls are conventionally considered identical since identical measures are used to prevent emission and block incoming electromagnetic noise.
In sum, RE Test is done to protect other systems from my system, and RS Test is done to protect my system from the outside. In some cases, both tests are needed when two or more modules exist in the same system and affect each other.
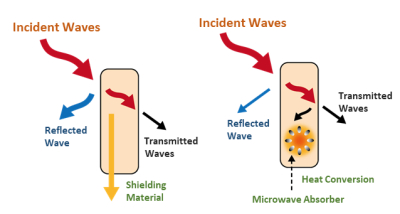
How to shield/suppress noise
We use an adequate mix of the following methods to prevent electromagnetic noise effectively. However, the noise cannot be completely removed; it is enough to partially remove it up to the required standard.
EMI Shielding
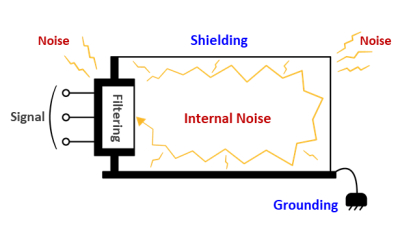
EMI shielding includes any measures to block electromagnetic noise and attenuate the acquired noise of a wire. In a narrow term, EMI shielding is achieving EMI and EMS solutions by wrapping or sealing the breaches in the target device using highly reflective materials, commonly metals of low resistance.
High-frequency waves could be effectively blocked using metals of low resistance in an adequate thickness, such as silver, copper, and aluminum, since they reflect most of the high-frequency waves. Otherwise, low-frequency waves and magnetic fields could be blocked using high permeability metals, such as iron, nickel, and cobalt.
PCB Grounding
Grounding means electrically connecting electronic devices to the ground to prevent electric shock, considering the earth as a massive conductor with zero electric potential.
Two kinds of grounding methods exist; Frame grounding means attaching the devices to a frame that will work as a ground reference potential when connecting to the ground is physically impossible. Signal grounding is a ground that PCB circuits use. The core thought of signal grounding is to expand the grounding area by electrically connecting PCB and the frame. If the signal grounding area is not sufficiently expanded, it will cause malfunction and unwanted radiation of EMI.
EMI Absorbing (EMI Suppression)
EMI absorbing (EMI suppression) converts radio wave energy into thermal energy using the principles of magnetic loss, dielectric loss, and conduction loss.
EMI absorber (EMI suppressor) is very versatile and can be used for various purposes.
By attaching an absorber to the inside of the metal frame (chassis), it is possible to prevent mutual interference of electromagnetic waves through the reflection of the frame and prevents signal overlap due to diffuse reflection inside the test box so that it can increase the accuracy of signal measurement.
When a thin sheet-type absorber is attached adjacent to the PCB pattern, high-frequency noise flowing through the circuit can be filtered by the high inductance acting as an impedance, and absorber can also be used as a ferrite core if it is wound on one part of the wire in the form of a narrow ribbon.